PD-1 Inhibitor Drugs Industry Forecast to Reach USD 179.77 Billion by 2034
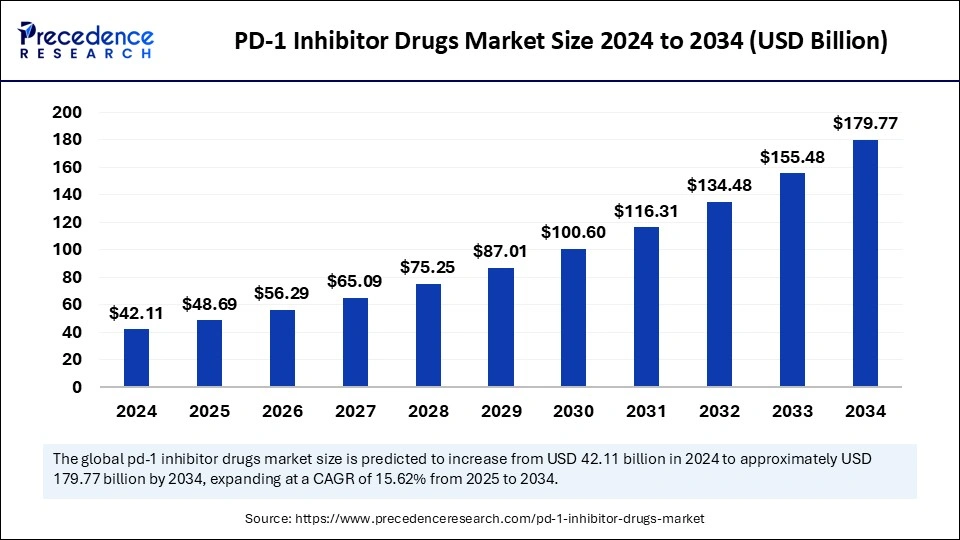
The global PD-1 inhibitor drugs industry is forecasted to grow from USD 42.11 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 179.77 billion by 2034, driven by a strong CAGR of 15.62% over the next decade.
PD-1 Inhibitor Drugs Industry Key Insights
- North America dominated the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth during the forecasted years.
- By drug type, the pembrolizumab segment contributed the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By drug type, the nivolumab segment is expected to show considerable growth in the forecast period.
- By indication, the non-small cell lung cancer segment dominated the market in 2024.
- By indication, the melanoma segment is anticipated to witness significant growth over the studied period.
- By distribution channel, the hospital pharmacies segment contributed the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By distribution channel, the online pharmacies segment is expected to show considerable growth in the forecast period.
The PD-1 (programmed cell death protein 1) inhibitor drugs market is experiencing remarkable growth, driven by increasing demand for immunotherapy treatments in oncology and autoimmune diseases. PD-1 inhibitors are a class of immune checkpoint inhibitors that work by blocking the PD-1 protein on T-cells, preventing cancer cells from evading the immune system. These drugs have revolutionized cancer treatment by offering targeted therapies with improved survival rates compared to traditional chemotherapy and radiation. Leading pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in PD-1 inhibitors due to their efficacy in treating various cancers, including lung cancer, melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
The market for PD-1 inhibitors has been expanding due to continuous advancements in immunotherapy, increasing prevalence of cancer, and growing clinical trials exploring their potential in non-cancerous conditions. The introduction of combination therapies, where PD-1 inhibitors are used alongside chemotherapy or other immunotherapies, has further enhanced treatment outcomes. Moreover, the growing acceptance of precision medicine and biomarker-based therapies has led to a surge in personalized treatment approaches, further boosting the adoption of PD-1 inhibitors. The global PD-1 inhibitor drugs market was estimated at USD 42.11 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately USD 179.77 billion by 2034, reflecting a robust CAGR of 15.62% over the forecast period.
Sample Link: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/sample/5718
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market is the rising global burden of cancer. Cancer remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, with increasing incidence rates due to factors such as aging populations, lifestyle changes, and environmental influences. Traditional cancer treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation, often come with significant side effects and limited efficacy, prompting healthcare providers to explore more effective alternatives like immunotherapy. PD-1 inhibitors have shown superior outcomes in various cancers by boosting the body’s immune response, leading to better survival rates and fewer adverse effects compared to conventional treatments.
Regulatory approvals and expanded indications for PD-1 inhibitors are also fueling market growth. Leading drugs such as Keytruda (pembrolizumab) and Opdivo (nivolumab) have received approvals for multiple cancer types, broadening their applications and increasing their adoption worldwide. Pharmaceutical companies are aggressively conducting clinical trials to secure approvals for new indications, further driving market expansion. Additionally, favorable reimbursement policies in developed countries, particularly in North America and Europe, have facilitated access to these drugs, making them a preferred choice for both patients and healthcare providers.
The increasing focus on combination therapies has also played a crucial role in market growth. Researchers have found that combining PD-1 inhibitors with other immunotherapies, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies significantly enhances their effectiveness. This has led to a growing number of clinical trials exploring novel drug combinations, resulting in improved treatment regimens and expanded market opportunities.
Opportunities
The PD-1 inhibitor drugs market presents significant opportunities for growth, particularly in emerging economies where healthcare infrastructure is rapidly improving. Countries such as China, India, and Brazil are witnessing increasing investments in cancer treatment facilities, along with rising awareness about immunotherapy. As governments and private healthcare providers in these regions focus on expanding access to advanced cancer treatments, the demand for PD-1 inhibitors is expected to surge.
Another key opportunity lies in the expansion of PD-1 inhibitors beyond oncology. While these drugs have primarily been used for cancer treatment, ongoing research suggests their potential in treating autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus. The ability of PD-1 inhibitors to regulate immune responses makes them a promising option for conditions where immune system dysfunction plays a critical role. Pharmaceutical companies are actively exploring new therapeutic areas, which could significantly expand the market beyond cancer treatment in the coming years.
Technological advancements in drug development and biomarker research are also opening new doors for PD-1 inhibitors. The emergence of precision medicine and companion diagnostics is enabling the identification of patients who are most likely to respond to PD-1 inhibitors, improving treatment efficacy and reducing unnecessary drug administration. Advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) and liquid biopsy technologies are helping identify specific genetic mutations and biomarkers that can predict patient response to immunotherapy, further optimizing treatment strategies.
The rise of biosimilars also presents a lucrative opportunity for the market. As patents for key PD-1 inhibitors expire in the coming years, several pharmaceutical companies are developing biosimilar versions to offer cost-effective alternatives. This could lead to increased accessibility and affordability, particularly in price-sensitive markets, further driving adoption rates.
Challenges
Despite its promising growth trajectory, the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market faces several challenges. One of the major hurdles is the high cost of treatment, which limits accessibility for many patients, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. PD-1 inhibitors are among the most expensive cancer therapies, with annual treatment costs often exceeding tens of thousands of dollars per patient. While insurance coverage and reimbursement policies have helped offset some of these costs in developed countries, affordability remains a significant issue in many parts of the world.
Another challenge is the development of resistance to PD-1 inhibitors. While these drugs have shown remarkable efficacy in many patients, some individuals develop resistance over time, leading to treatment failure. Researchers are working to understand the mechanisms behind resistance and develop strategies to overcome it, including novel drug combinations and next-generation immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, addressing this issue remains a complex and ongoing challenge.
Regulatory hurdles also pose challenges for market players. The approval process for new PD-1 inhibitors and combination therapies can be lengthy and complex, requiring extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Additionally, stringent regulatory requirements in different regions create barriers to market entry, particularly for smaller biotech firms.
Competition within the PD-1 inhibitor market is intensifying as more pharmaceutical companies enter the space. While established players such as Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche dominate the market, new entrants and biosimilars are increasing competition, potentially leading to pricing pressures and reduced profit margins for existing drugs.
Regional Insights
North America currently dominates the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market, driven by high cancer incidence rates, well-established healthcare infrastructure, and strong regulatory support. The United States is the largest contributor to market growth, with leading pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in research and development. Favorable reimbursement policies and widespread adoption of immunotherapy further strengthen the market position in this region.
Europe is another significant market for PD-1 inhibitors, with countries like Germany, France, and the United Kingdom leading in terms of immunotherapy adoption. The presence of strong regulatory frameworks, increasing clinical trials, and government initiatives promoting cancer research contribute to market growth. However, pricing and reimbursement challenges remain key concerns in some European nations.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the PD-1 inhibitor market due to rising cancer prevalence, improving healthcare access, and growing pharmaceutical investments. China, in particular, has emerged as a major player in the immunotherapy space, with domestic companies developing PD-1 inhibitors and securing regulatory approvals. Japan and South Korea are also at the forefront of immunotherapy advancements, further driving regional market expansion.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are still in the early stages of PD-1 inhibitor adoption, primarily due to limited healthcare infrastructure and high drug costs. However, increasing awareness about cancer treatments and government efforts to improve healthcare access could drive future growth in these regions.
Read Also: Dental Support Organizations Market
Market Companies
- Akeso Inc.
- Alphamab Oncology
- Amgen Inc.
- AstraZeneca Plc
- BeiGene Ltd.
- Bristol Myers Squibb Co.
- Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd.
- Eli Lilly and Co.