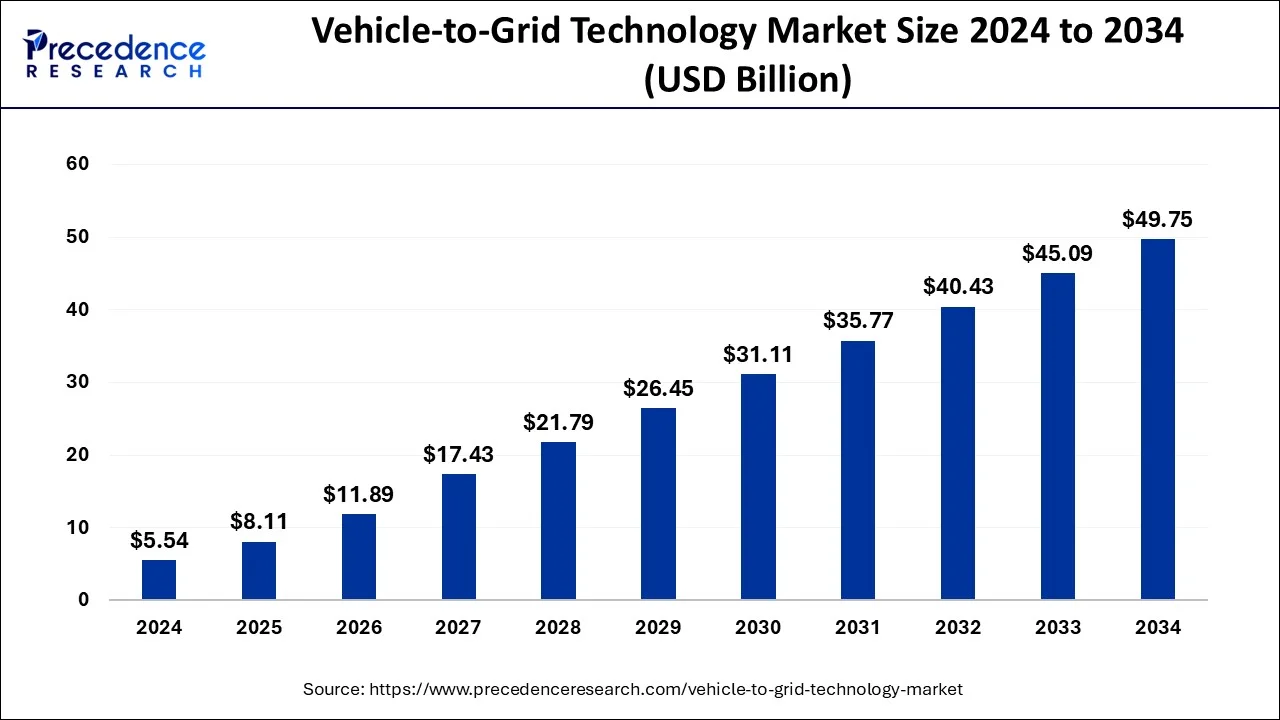
Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market to Reach USD 49.75 Bn by 2034.
The global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, valued at USD 5.54 billion in 2024, is expected to reach USD 49.75 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 28.13%.
Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Key Insights
- Regional Leadership: Europe dominated the global market in 2024, holding the highest market share of approximately 35.80%.
- Component Type: The electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) segment accounted for the largest revenue share, reaching 83.13% in 2024.
- Application – BEVs: The battery electric vehicles (BEVs) segment led the market with a significant share of 63.89% in 2024.
- Application – PHEVs: The plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) segment is projected to grow at an impressive CAGR of 28.59%.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is revolutionizing the way we think about energy and transportation. By enabling electric vehicles (EVs) to not only draw power from the grid but also supply it back, V2G creates a dynamic energy exchange that enhances grid stability and offers potential financial benefits to EV owners. This bidirectional flow transforms vehicles into mobile energy storage units, contributing to a more resilient and efficient energy system.
Sample Link: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/sample/1019
Market Drivers
The surge in EV adoption, driven by environmental concerns and supportive policies, has been a significant catalyst for the V2G market. As more renewable energy sources like solar and wind are integrated into the grid, the need for flexible energy storage solutions becomes paramount. V2G addresses this by allowing stored energy in vehicles to be fed back during peak demand, thus balancing supply and demand effectively. Moreover, advancements in battery technology and the decreasing costs of EVs make V2G an attractive proposition for consumers and utilities alike.
Opportunities
Opportunities within the V2G landscape are vast. For consumers, there’s the potential to offset energy costs by selling excess power back to the grid. Utilities benefit from improved grid management and reduced reliance on fossil-fuel-based peaking power plants. Additionally, V2G can play a pivotal role in emergency situations, providing backup power during outages. The technology also opens avenues for new business models, such as energy-as-a-service, where companies manage the energy transactions between EVs and the grid on behalf of users.
Challenges
However, the path to widespread V2G adoption is not without challenges. A significant hurdle is the lack of standardized protocols and regulatory frameworks, leading to uncertainties for stakeholders and complicating integration efforts. Consumer awareness remains limited, and concerns about battery degradation persist, despite studies suggesting minimal impact. Infrastructure development, including the availability of affordable bidirectional chargers, is still in its nascent stages, requiring substantial investment and coordination among various sectors.
Regional Insights
Regionally, the V2G market exhibits varied dynamics. In North America, particularly the United States, initiatives are underway to incorporate V2G into school bus fleets, turning them into energy assets during off-school hours. Europe sees collaborative efforts among automakers and energy companies to develop V2G-compatible vehicles and infrastructure. In Asia-Pacific, countries like Japan are at the forefront, with companies investing in technologies that facilitate seamless energy exchange between vehicles and the grid. Each region’s approach is shaped by its unique energy policies, market maturity, and technological readiness.
Read Also: Electric Vehicle Charging Cables Market